Simple and hassle-free treatment – Dr Bhavna Patel
Featured Products Promotional FeaturesPosted by: Dental Design 14th October 2019

 Dr Bhavna Patel highlights the benefits of anterior alignment orthodontic case when discretion of treatment is important for the patient.
Dr Bhavna Patel highlights the benefits of anterior alignment orthodontic case when discretion of treatment is important for the patient.
A male patient presented with concerns regarding the appearance of his upper and lower anterior teeth. He had undergone comprehensive orthodontic treatment as a teenager but had recently noticed that his teeth were gradually becoming more and more crowded, especially in the right anterior segment.
The patient’s job as an actor meant that he was looking at images of himself very closely. Therefore, the imperfections really stood out to him and he wanted to do something about them, but sought treatment that wouldn’t affect his work.
Assessment and treatment planning
Various single and dual arch orthodontic options were discussed, alongside potential referral to a specialist orthodontist for comprehensive treatment. Due to the patient’s profession, fixed or comprehensive orthodontics were not suitable. He had seen some of his colleagues undergo treatment with removable appliances and was interested in something similar. We discussed possible treatment options with the Inman Aligner or ClearSmile Aligners, including all benefits and limitations of the appliances.
A thorough dental and orthodontic assessment was carried out (Table 1), including full IAS Academy protocol photos and digital calliper measurements. Using Spacewize™+ digital crowding calculator software, the space requirement and the patient’s suitability for treatment with Inman Aligner was confirmed.
Table 1 – Assessment
| Skeletal | Class II | |
| FMPA | Average | |
| Lower face height | Average | |
| Facial asymmetry | No | |
| Soft tissues | Average nasolabial angle, lips competent at rest | |
| Overjet | Average | |
| Overbite | Slightly reduced | |
| Crossbite | No | |
| Displacement on closure | No | |
| Incisor relationship | Class I | |
| Molar relationship | Right 1/4unit Class III | Left ½ unit Class III |
| Canine relationship | Class I | Class I |
| Teeth present | 765321 | 1234567 |
| 765321 | 1234567 | |
| Centrelines | Not coincident, with lower approximately 2mm to right of upper | |
The aim of treatment was to use the Inman Aligner to first align the lower anterior segment, followed by the upper anterior segment. Archwize™ 3D planning software was used to predict the amount of interproximal reduction (IPR) that would be required to achieve the intended results. This was discussed with the patient to demonstrate what we could achieve and what the likely compromises were going to be, prior to obtaining informed consent (Table 2).
To complete treatment, tooth whitening and composite edge bonding post-alignment were discussed. The patient consented to alignment and edge bonding of the UR2 to restore the worn incisal edge. However, he was happy with the colour of his teeth and did not want any whitening.
Table 2 – Ideal versus compromised treatment aims
| Problem List |
| Mild crowding, slightly retroclined upper right lateral incisor |
| Slightly collapsed buccal corridor on right hand side |
| Slightly reduced overbite |
| Crowding of lower anterior segment |
| Ideal Treatment Aims : |
| Correct upper and lower crowding, and torque teeth to ideal angulation |
| Correct canine and molar relationship into class I |
| Correct reduced overbite |
| Restore worn incisal edge of the UR2 |
| Compromise Treatment Aims: |
| Correct upper and lower anterior segment crowding |
| Accept canine and molar relationship |
| Improve overbite |
| Restore worn incisal edge of the UR2 |
Treatment sequence
Following the initial consultation and assessment, an ArchwizeTM 3D plan was created by the IAS Laboratory using upper and lower PVS impressions, a bite registration and the prescription sent to them. A lower Inman Aligner was fabricated following approval, with an estimated 2.8mm of IPR required for the lower arch. Half the IPR was carried out at the fit appointment along with placement of lingual composite anchors on the lower laterals and posterior bite guards were provided.
The patient was reviewed at 2-4 weekly intervals for further IPR, removal of bite guards and replacement of composite anchors as required. Retracted and occlusal photos were taken at each appointment to help monitor case progression. The desired lower alignment was achieved in approximately 20 weeks, when a lower inter-canine bonded retainer was placed.
The upper Inman Aligner fabrication was approved when the impression for the lower bonded retainer was sent to the IAS laboratory. A total of 0.7mm IPR was required in the upper arch, of which half was carried out on the day the Inman Aligner was fitted. The patient was again reviewed at 4 weekly intervals for further IPR and replacement of composite anchors as required. The desired alignment was achieved in approximately 18 weeks. The upper inter-canine bonded retainer was placed and the UR2 composite edge bonding was performed.
Outcome and case appraisal
Overall, I feel a great result was achieved. I may have initially been a little hesitant with the IPR, so progress might have been quicker otherwise. Upon critical reflection – although it wasn’t something that had been an issue or discussed – maybe edge bonding the UR3 could have created a more symmetrical result.
The patient was very happy with the outcome and feels great about his smile now. He felt that the Inman Aligner treatment was simple and hassle-free. Furthermore, being able to remove the aligner when needed meant that it did not interfere with his work as an actor.
I would like to thank the IAS Academy mentors and lab team for their continued help and support in helping me deliver minimally invasive high-quality results.
IMAGES
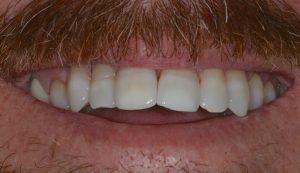
Figure 1 – Pre treatment smile
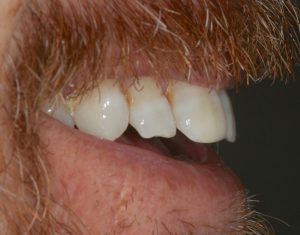
Figure 2 – Pre treatment right view
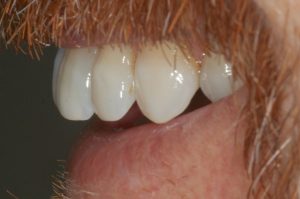
Figure 3 – Pre treatment left view
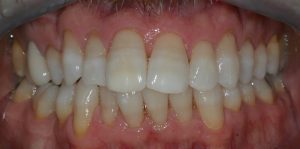
Figure 4 – Pre treatment retracted view
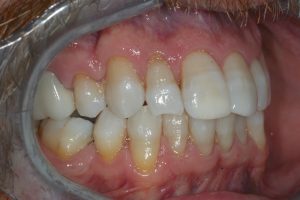
Figure 5 – Pre treatment right lateral view
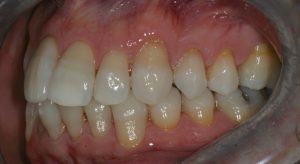
Figure 6 – Pre treatmen tleft lateral view
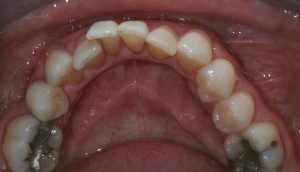
Figure 7 – Pre treatment lower occlusal view
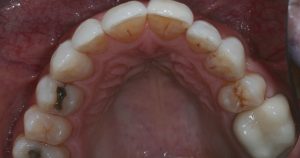
Figure 8 – Pre treatment upper occlusal view
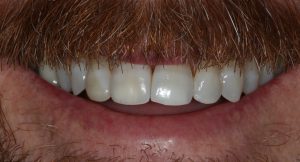
Figure 9 – Post treatment smile
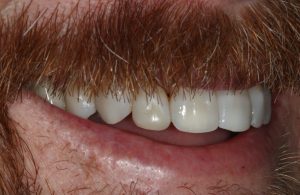
Figure 10 – Post treatment right view
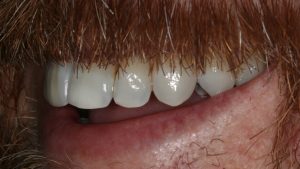
Figure 11 – Post treatment left view
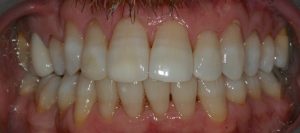
Figure 12 – Post treatment retracted view
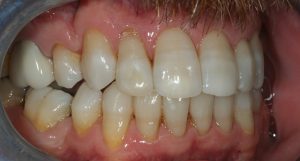
Figure 13 – Post treatment right latreal view
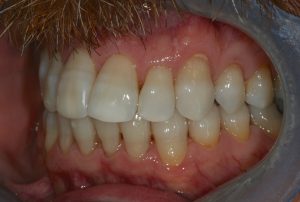
Figure 14 – Post treatment left lateral view
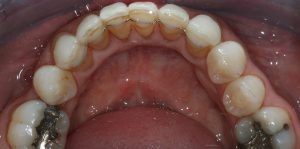
Figure 15 – Post treatment lower occlusal view
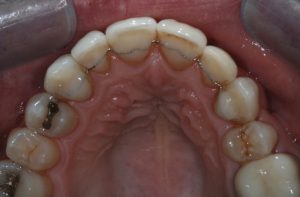
Figure 16 – Post treatment upper occlusal view
For more information on upcoming IAS Academy training courses, including those for the Inman Aligner and Aligner system, please visit www.iasortho.comor call 01932 336470 (Press 1)
Author bio:
Dr Bhavna Patel BDS MFDS RCS (Eng) is an associate dental surgeon working in mainly private practices – Roseneath Dental Surgery in Byfleet and Bupa Dental Care in Woking, Surrey. She has a particular interest in anterior alignment orthodontics and minimally invasive cosmetic dentistry, especially composite bonding.
No Comments
No comments yet.
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.



